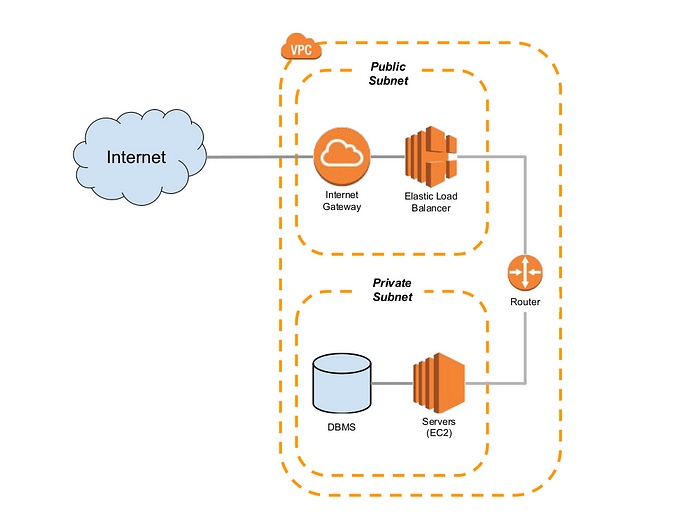
Amazon Web Services (AWS) Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) is a service that allows you to create a private, isolated network within the AWS cloud. With VPC, you can launch resources in a virtual network that you define. VPC provides you with complete control over your virtual networking environment, including IP addressing, subnets, routing tables, and network gateways.
Why use AWS VPC?
AWS VPC allows you to create a secure and isolated network for your resources, which provides a high level of security and control. This means that you can create your own private network, which is not accessible from the internet or other networks. AWS VPC also enables you to create a VPN connection between your on-premises infrastructure and your AWS VPC. This connection allows you to access resources in your VPC from your on-premises infrastructure.
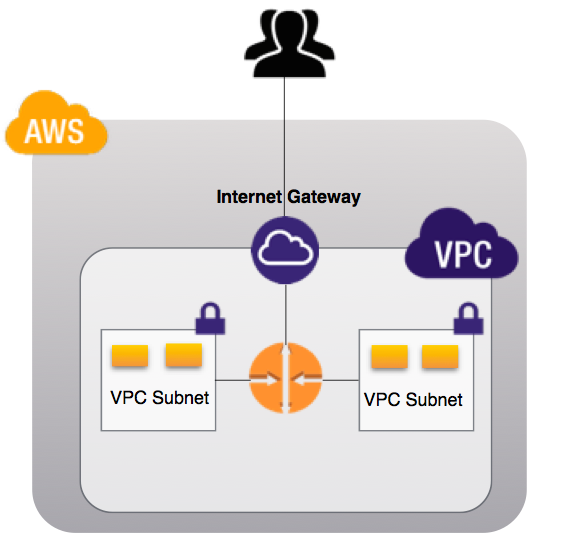
AWS VPC Components:
- Subnets: A subnet is a range of IP addresses in your VPC. You can launch resources, such as EC2 instances and RDS databases, in a subnet. You can also assign different subnets to different availability zones to achieve high availability and fault tolerance.
- Route Tables: A route table is a set of rules that determines how traffic is directed in your VPC. You can create multiple route tables and assign them to different subnets to control the flow of traffic.
- Internet Gateway: An internet gateway is a horizontally scaled, redundant, and highly available VPC component that allows communication between instances in your VPC and the internet.
- NAT Gateway: A network address translation (NAT) gateway enables instances in a private subnet to connect to the internet or other AWS services while preventing the internet from initiating connections with the instances.
- Security Groups: Security groups act as a virtual firewall for your instances. You can create security groups to control inbound and outbound traffic for your instances.
- Network Access Control Lists (NACLs): NACLs are another layer of security that act as a firewall for subnets. You can use NACLs to control inbound and outbound traffic at the subnet level.
Creating your own VPC:

Under Your VPCs, click on Create VPC
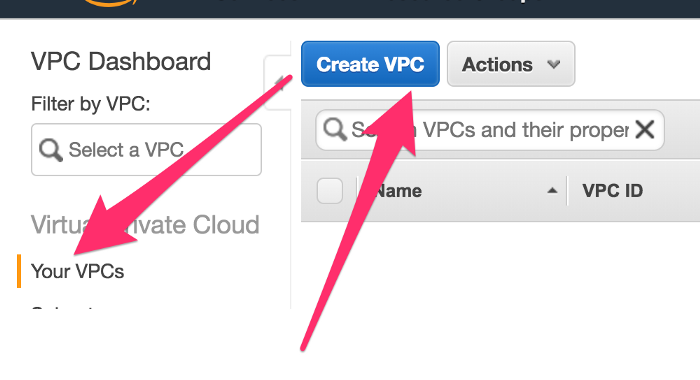
Fill all the details(Name and IPv4 CIDR block, depending upon the network range you want, leave all the other details as default or depend upon your requirement, i.e whether you need IPv6 or Tenancy default or dedicated)and then click Yes,Create
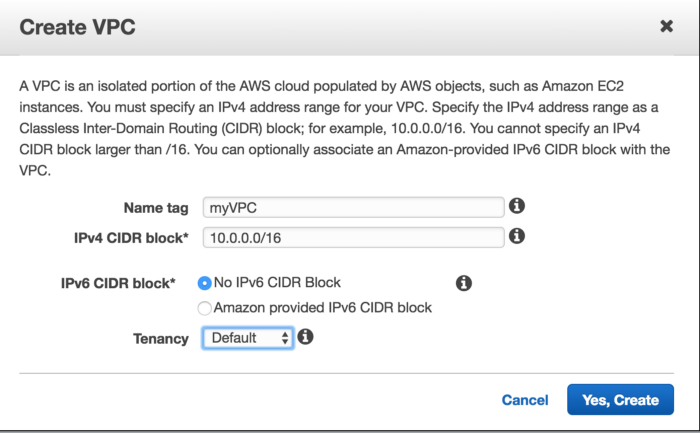
As soon as we create our default VPC, aws will create
Route Table
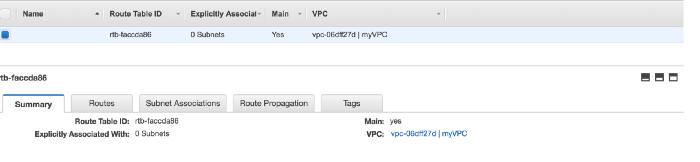
Network ACLs
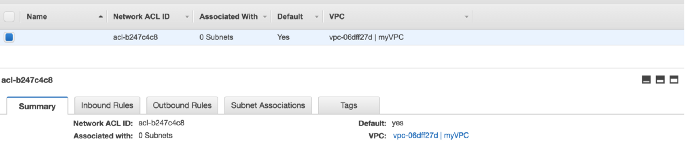
Security Group
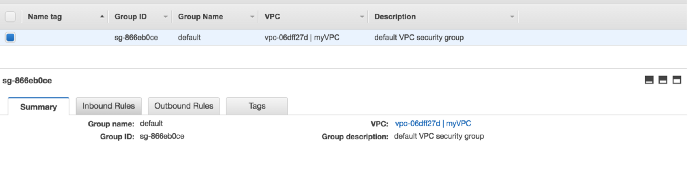
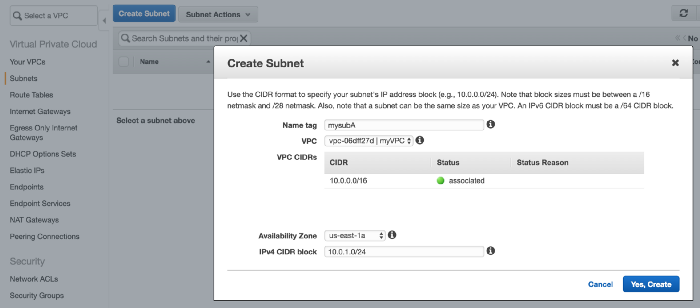
Next step is to create subnet
Click on Subnet and then Create Subnet
Similarly create second subnet
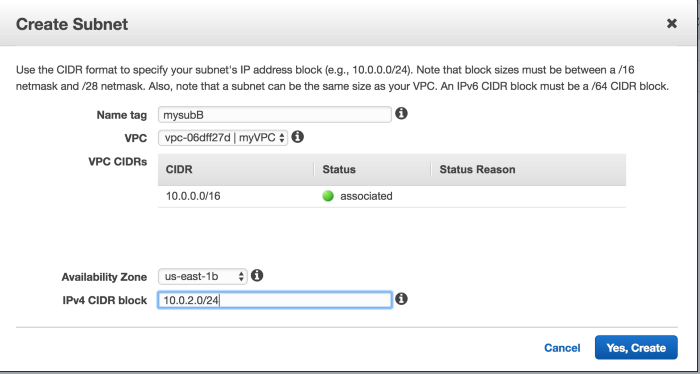
This is how it look like

Next create internet gateway so that we have some sort of internet connectivity
Go to Internet Gateways → Create internet gateway
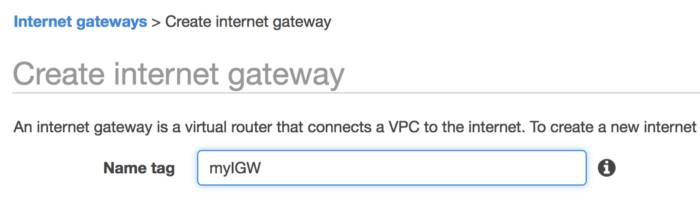
Give it a Name tag
Next create internet gateway so that we have some sort of internet connectivity
Go to Internet Gateways → Create internet gateway
Give it a Name tag
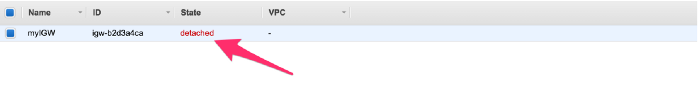
By default it’s automatically detached
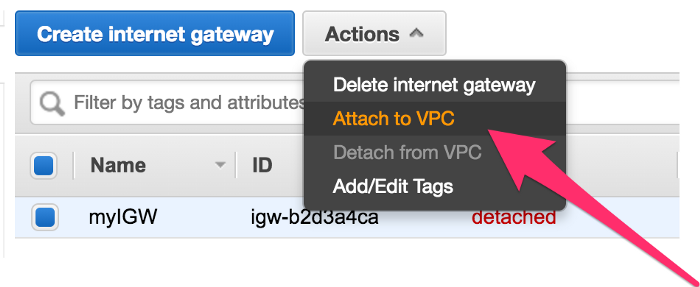
To attach it to VPC, go to action and click on Attach to VPC
It will ask you which VPC to attach
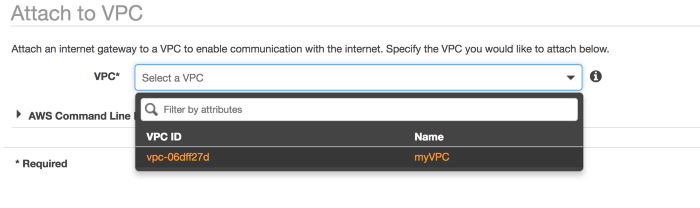
Provide the VPC name you are building
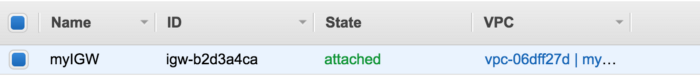
P.S: Once again we can only have one IGW per VPC
Next step to go to Route table
We only have one route table which allow local communication between subnet
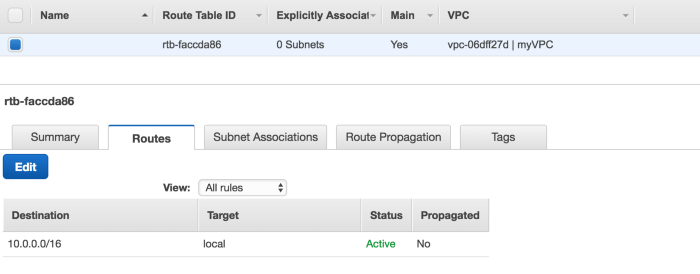
Go to next tab,Subnet Associations under Route Table
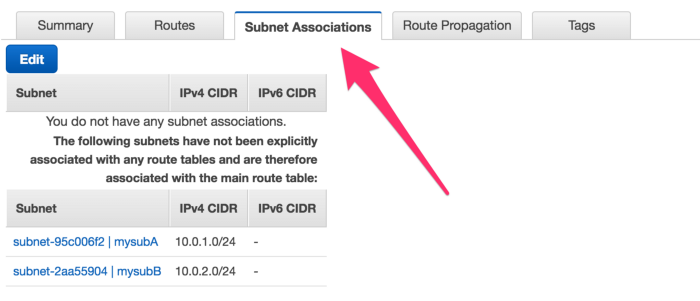
As you can see these subnet are not associated with any route table(except with main route table), which is good as every-time we create a new subnet it will be associated with main route table and that’s why we don’t want our route table to have access to the internet.
So let’s create new Route Table, by clicking on Create Route Table
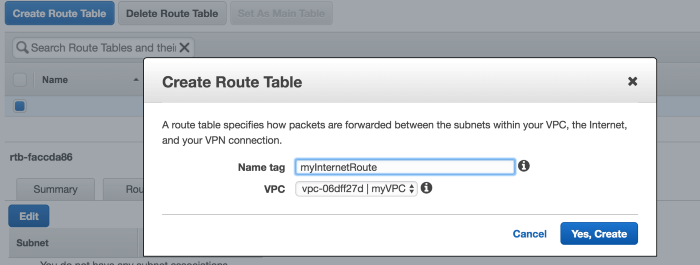
For this route table let’s enable route access(Go to Routes and Add another route)
Destination: 0.0.0.0/0
Target: igw-b2d3a4ca(internet gateway)
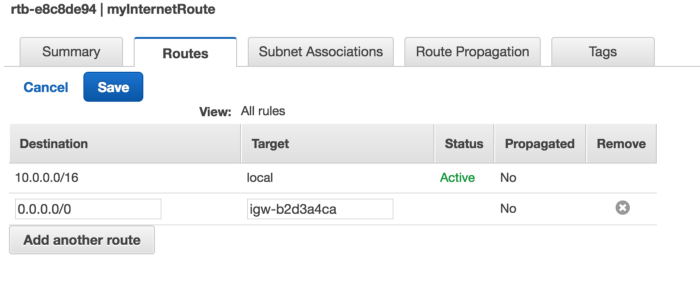
This will give us internet accessibility
Now we can associate one subnet with this route table(Click on Subnet Association → choose one subnet)
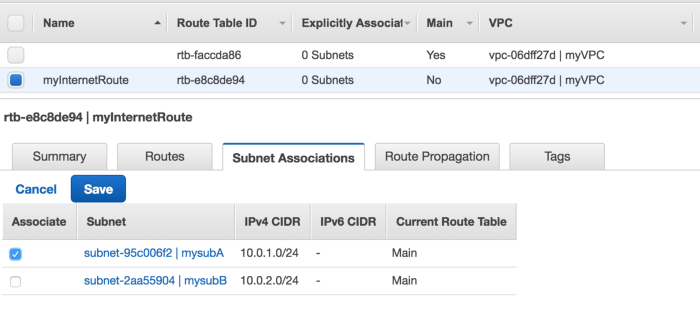
So 10.0.1.0/24 is now our public subnet
Let spun up two servers one in Public Subnet(10.0.1.0/24) and one in Private Subnet(10.0.2.0/24). But before doing that we are missing one piece. Go back to subnet tab and as you can Auto-assign Public IP is set to No
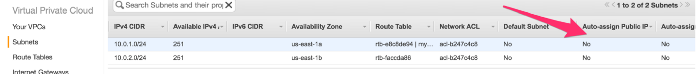
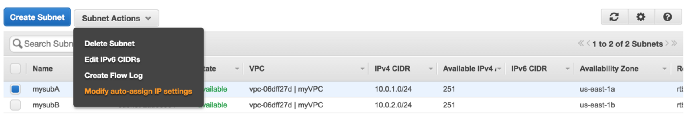
For Public Subnet,Modify the auto-assign IP settings under Subnet Actions
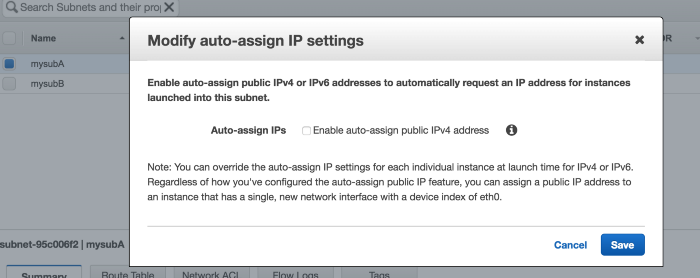
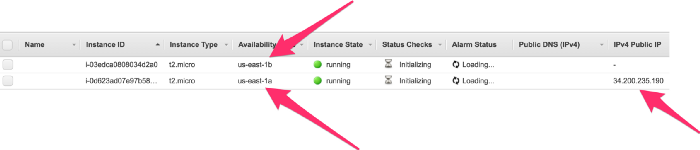
As you can see I spun up 2 instances one in Public Subnet(10.0.1.0/24) and one in Private Subnet(10.0.2.0/24). Public Subnet one got the Public IP
NAT Gateway
Network address translation (NAT) gateway is used to enable instances in a private subnet to connect to the internet or other AWS services, but prevent the internet from initiating a connection with those instances
To create a NAT gateway, go back to VPC and click on NAT Gateways
Click on create NAT Gateway
Make sure you select the Public Subnet
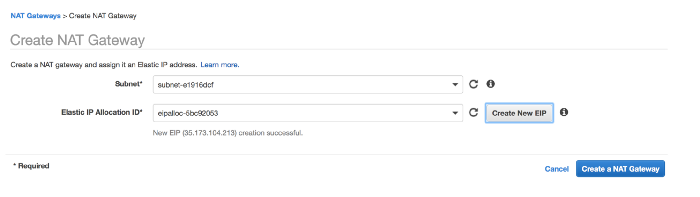
Once NAT gateway is available, go back to your Default Route table and add a route, with Target as NAT gateway.
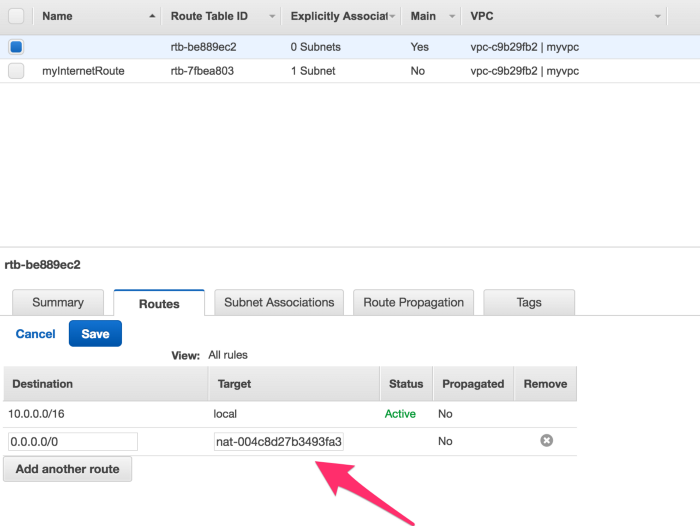
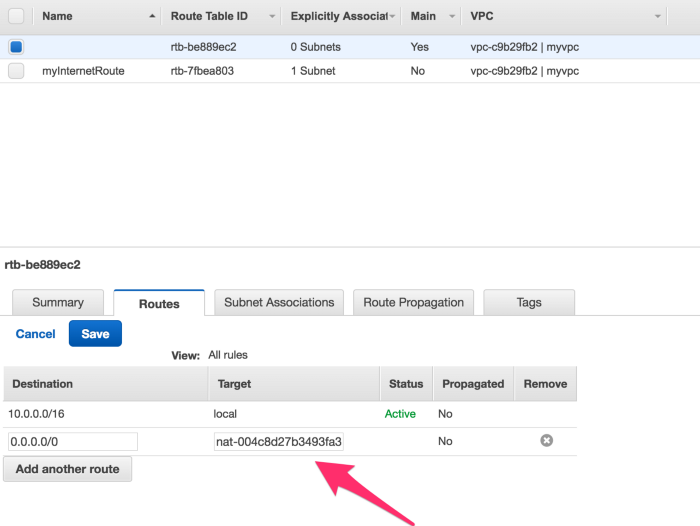
Network ACL
A network access control list (ACL) is an optional layer of security for your VPC that acts as a firewall for controlling traffic in and out of one or more subnets. You might set up network ACLs with rules similar to your security groups in order to add an additional layer of security to your VPC
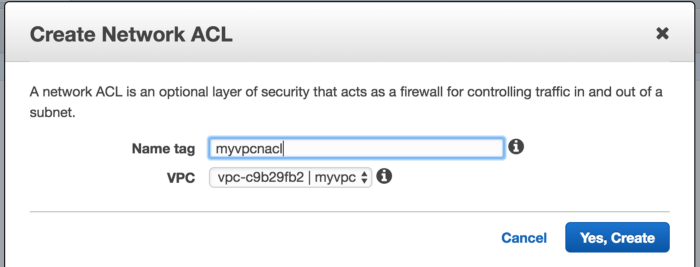
To create a NACL, go to Network ACLs under VPC and click on Create Network ACL
NOTE: Under default NACL everything is allowed by default
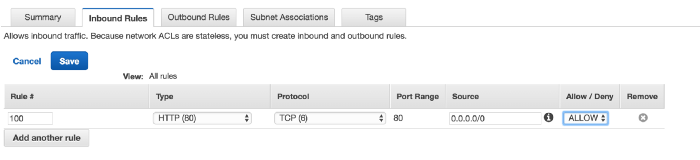
Now if we check the Inbound rule under this NACL, everything is denied by default
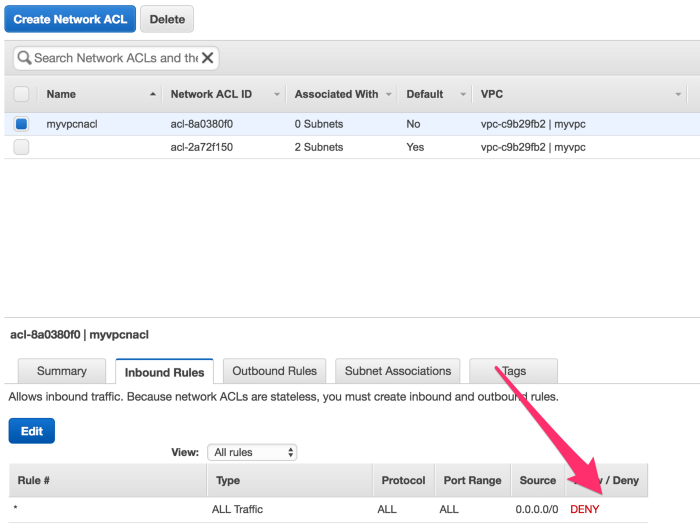
To add a rule
Conclusion:
AWS VPC is a highly customizable networking service that provides a secure and isolated environment for your resources. With subnets, route tables, internet gateways, NAT gateways, security groups, and NACLs, you can design a VPC that meets your specific requirements. Each component in VPC provides a unique functionality that enables you to control and secure the flow of traffic in your VPC. By leveraging these components, you can build a highly available, fault-tolerant, and secure VPC that meets your organization’s networking needs.
Comments